
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/19989784/Recovery_screen.png)
Definitely worth keeping in mind if you’ve seen someone overclock your CPU to a certain speed. It can sometimes be the case that whilst one person’s CPU will overclock to a certain GHz, another person’s might not be able to get anywhere near that speed. However, if you know what you are doing and have the correct cooling methods in place, overclocking will not pose as a problem.Įach individual CPU is different regardless of whether they are the same model number from a manufacturer. Manufacturers tend to be conservative with their ‘out-of-the-box’ clock speeds to ensure that the CPUs do not overheat for the average consumer. And whilst it can most definitely speed up your system, it can often be quite complicated.įor example, overclocking an Intel Core i7 860 that normally runs at around 2.80GHz out the box can mean that you get well over 2.80GHz out of it. Overclocking is where you push your computers components harder and faster than the manufacturers intended them to go. If you are dealing with more than 64 Logical Processors under Windows then that introduces Processor Groups and that add another layer of options.One of the more complicated ways to get increased performance from your CPU is to overclock it.
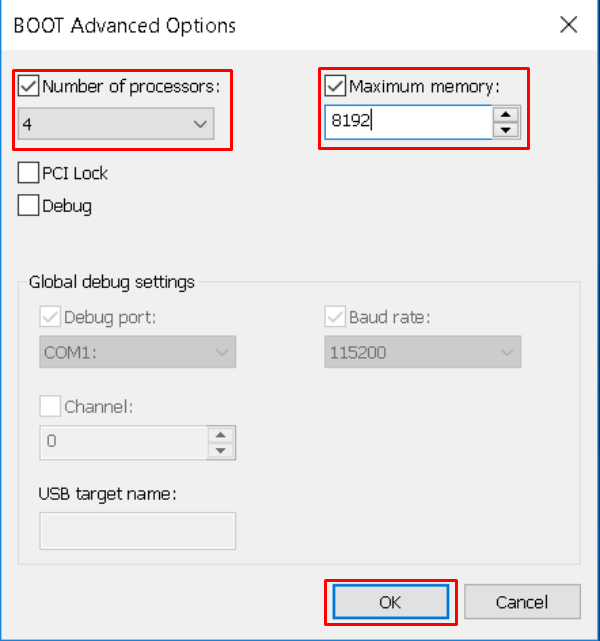
In this example itc creates a maximum number of processors of 8.

The easiest way in Windows to reduce the LP count is to use the /NUMPROC option. Windows recognises logical processors (LP) as the basic compute platform - giving one LP for each hyperthread within a core, and then multiplied for each core, which is finally multiplied by the number of sockets. Does the processor refer to a threads (from Hyperthreading), cores, or sockets (physical CPUs). In an era of multi-core, hyperthreaded CPUs, "Processors" is now an ambiguous term.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
